Top 10 Welding Wire Types You Need to Know for Your Next Project
When embarking on a welding project, understanding the different types of welding wire available is crucial for achieving optimal results. The choice of welding wire can significantly influence the quality, strength, and appearance of the weld, making it essential to select the right type for specific applications. Each type of welding wire is designed to work with different materials and welding processes, ensuring that welders can attain the desired performance and finish.
In this guide, we will delve into the top 10 welding wire types you need to know for your next project. From mild steel to stainless steel and aluminum, these welding wires cater to a variety of industries and applications. By familiarizing yourself with these options, you will be better prepared to select the most suitable welding wire that meets your project requirements, enhances your workflow, and delivers lasting results. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a novice welder, understanding the nuances of different welding wires is a vital step in your journey toward mastering the art of welding.
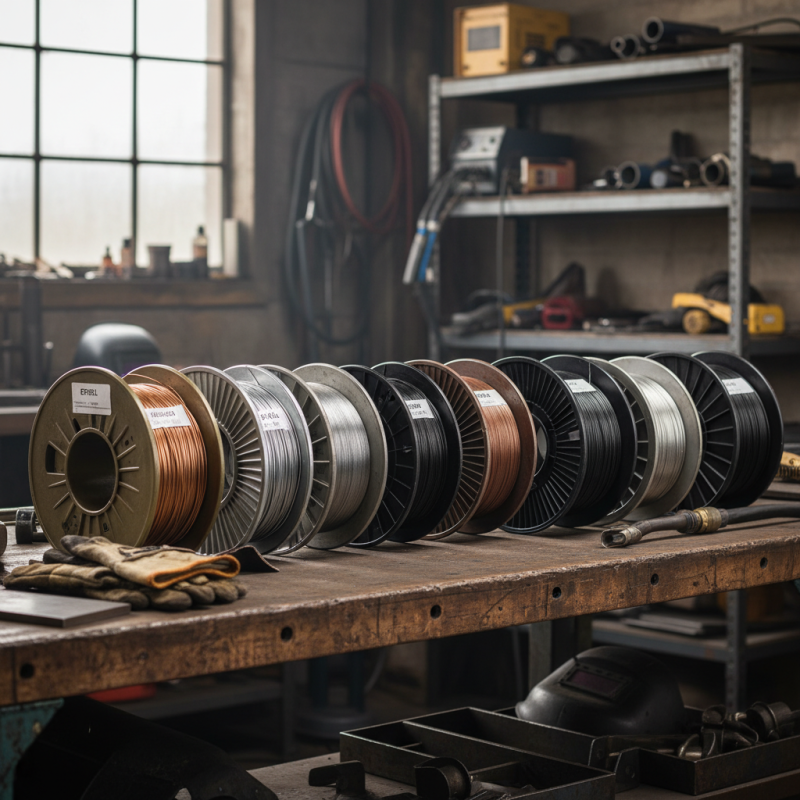

Understanding Welding Wire Basics and Their Importance in Projects

Understanding welding wire and its varied types is crucial for achieving optimal results in any welding project. Welding wire serves as a filler material that bonds two or more metals together, ensuring structural integrity and durability. Different projects may necessitate specific types of welding wire, primarily influenced by the materials being welded, the welding technique employed, and the desired properties of the finished joint. According to industry reports, selecting the appropriate welding wire can enhance joint strength by up to 20%, significantly impacting the overall quality and performance of the welded assembly.
The most common types of welding wires include ER70S-6, commonly used for mild steel applications, and ER308L, ideal for stainless steel welding. Each wire type has distinct characteristics tailored for specific materials and conditions, including corroding environments or high-stress applications. Research indicates that using the correct welding wire type can reduce defects in the welds by as much as 30% compared to using an inappropriate wire. With advancements in metallurgy, new wire formulations continue to enter the market, expanding possibilities for welders to achieve superior results while meeting industry standards and safety regulations. Therefore, understanding the fundamentals of welding wire is not just essential; it's a pivotal aspect of successful welding practices in today's construction and manufacturing sectors.
Common Types of Welding Wires and Their Specific Applications
Welding wire is a crucial component in the metal joining process, with different types of wires tailored for specific applications and materials. Among the most common types, mild steel wire is widely used due to its versatility and strength. According to the American Welding Society, mild steel wires account for nearly 70% of all welding wire consumed in various industries, making them the backbone of fabrication projects. These wires are suitable for applications ranging from automotive manufacturing to construction, where durability and weld quality are paramount.
Stainless steel wire, another prevalent type, is essential for projects requiring corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Particularly in food processing, chemical production, and marine applications, stainless steel wires enhance the longevity and performance of welds. Reports indicate that the demand for stainless steel welding wire has increased steadily, reflecting a broader trend in industries prioritizing hygiene and resilience. Furthermore, flux-cored wires have gained traction in construction and repair due to their high deposition rates and efficiency in various positions, making them ideal for heavy-duty welding applications. The versatility and performance specifications of these wire types underline their significance in achieving successful welding outcomes across diverse sectors.
Criteria for Choosing the Right Welding Wire for Your Project
When selecting the right welding wire for your project, several critical criteria come into play. First and foremost, consider the type of welding process you will be using—MIG, TIG, or stick welding—as each method typically requires specific wire types that complement their operational characteristics. For instance, MIG welding often employs solid or flux-cored wires, while TIG welding usually requires filler rods that match the base metal. Identifying the correct wire type is essential for achieving optimal weld quality and performance.
Another vital factor to consider is the material being welded. Different metals, such as steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, require specific welding wires tailored to their properties. For instance, using a wire designed for mild steel on stainless steel can lead to weak welds and corrosion issues. Additionally, pay attention to the wire diameter, as this directly affects the heat and penetration of the weld. A thicker wire is suitable for larger projects with high heat demands, while a thinner wire may be more appropriate for delicate tasks or thin materials. Understanding these criteria will help ensure you choose the best welding wire for a successful outcome in your welding endeavors.
Top 10 Welding Wire Types You Need to Know for Your Next Project
| Welding Wire Type | Material | Diameter (mm) | Suitable Processes | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER70S-6 | Mild Steel | 0.8 - 1.6 | MIG | General Steel Fabrication |
| ER308L | Stainless Steel | 0.8 - 1.2 | MIG, TIG | Food Processing, Chemical Industry |
| ER5356 | Aluminum | 1.0 - 2.4 | MIG, TIG | Marine Applications |
| E6010 | Mild Steel | 2.0 - 4.0 | Stick | Root Passes in Pipe Welding |
| E7018 | Mild Steel | 2.0 - 4.0 | Stick | Structural Welding |
| ER4047 | Aluminum | 1.0 - 2.4 | MIG, TIG | Automotive Applications |
| ER70S-2 | Mild Steel | 0.8 - 1.6 | MIG | Heavy Fabrication |
| ER316L | Stainless Steel | 0.8 - 1.2 | MIG, TIG | Marine Applications |
| FCW (Flux-Cored Wire) | Mild Steel | 1.0 - 2.4 | Flux-Cored | Outdoors and Windy Conditions |
| ER80S-B2 | Low Alloy Steel | 1.0 - 2.4 | MIG, TIG | High-Strength Welding |
Best Practices for Using and Storing Welding Wire
When it comes to using and storing welding wire, following best practices is crucial for both safety and efficiency. Proper storage conditions can significantly influence the integrity and performance of welding wire. For optimal results, welding wire should be kept in a dry, controlled environment to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to issues like rust and hydrogen embrittlement. According to a report from the American Welding Society, improper storage can decrease the effectiveness of welding materials by up to 25%, which can ultimately affect the quality of the welds.
Additionally, it's important to handle welding wire with care. Using gloves and protective gear when handling wire can reduce the risks of contamination from oils and other substances that may be present on hands. Furthermore, maintaining a clean workspace helps in preventing debris from affecting the wire, as contaminants can lead to problems such as porosity and inclusions in welds. Regularly checking the wire for signs of damage or wear before use is another best practice emphasized by industry experts, ensuring that only the best quality wire is utilized for each project. When these practices are adhered to, welders can achieve the highest standards in their work while prolonging the lifespan of the welding wire.
Top 10 Welding Wire Types
Safety Precautions When Working with Different Welding Wires
When working with different welding wires, it’s essential to prioritize safety to avoid accidents and health hazards. Welding can release harmful fumes and sparks that pose risks to your respiratory system and skin. Ensure you are working in a well-ventilated area or use appropriate fume extraction systems to minimize exposure to toxic substances. Additionally, always wear the right personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety goggles, and a welding helmet with the appropriate shade lens to protect against UV rays.
It’s also crucial to keep your workspace organized and free of flammable materials. Store welding wires and other materials in a safe manner that prevents accidents or ignition sources. Make sure to inspect your equipment regularly for any wear and tear that could lead to malfunctions or sparks. This proactive approach not only enhances your safety but also improves the quality of your welding work.
Tips: Before starting any welding project, familiarize yourself with the specific types of welding wire you will be using. Each wire type may have particular safety guidelines associated with it. Essential safety checks should include verifying gas connections and ensuring that your welding machine is functioning correctly. Always have a fire extinguisher nearby and know the emergency procedures in case of an accident.
Related Posts
-

Revitalize Your Cleaning Routine: Discover the Power of Steel Brushes for Every Task
-

Exploring the Impact of Wire Brush Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Innovative Trends and Market Insights for Welded Wire Mesh at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Stainless Steel Mesh Screen for Your Needs
-
Why You Should Choose Galvanized Wire Mesh for Your Next Project
-
Top Wire Brush Types to Choose for Effective Cleaning in 2025
